Introduction
Have you ever noticed how some days you wake up ready to conquer the world, while other days even the smallest tasks feel overwhelming? That’s the power of mood at work. Mood isn’t just a fleeting emotional state—it’s a complex interplay of brain chemistry, hormones, sleep patterns, gut health, environment, and even the people you surround yourself with. It influences how you think, make decisions, interact with others, and ultimately, how you experience life.
The good news? Mood isn’t entirely random. While genetics and circumstances play a role, science shows we can actively influence our emotional state through intentional choices and strategies—what we’ll call mood biohacks.
Mood biohacking means using tools, habits, and scientifically validated practices to optimize your brain chemistry and emotional resilience. Unlike quick fixes (like caffeine or sugar highs that crash later), these hacks aim at sustainable improvements. Whether through nutrition, sleep optimization, exercise, mindfulness, technology, or supplements, mood biohacking empowers you to take charge of your emotional well-being.
Why does this matter? Because mood impacts every area of life. Studies show positive mood enhances creativity, productivity, memory, and even physical health. Conversely, chronic low mood increases the risk of anxiety, depression, cardiovascular issues, and burnout. In today’s fast-paced, overstimulated world, knowing how to manage and elevate your mood isn’t just a luxury—it’s a survival skill.
In this guide, we’ll explore practical, science-backed mood biohacks across lifestyle, nutrition, supplements, technology, environment, and psychology. You’ll learn how to harness sleep, food, movement, breathwork, nootropics, and even light exposure to fine-tune your brain chemistry. We’ll also dive into cutting-edge approaches like neurofeedback, cold exposure, and wearable mood trackers.
Think of this as your playbook for emotional optimization—a toolkit you can experiment with, mix, and personalize. You don’t need to try everything at once; even one or two changes can create a noticeable difference. Over time, layering multiple biohacks compounds the effect, creating a powerful upward spiral for mood, health, and performance.
Ready to take charge of your emotional state? Let’s start by understanding the foundations of mood—what drives it, what disrupts it, and how to hack it at the root level.
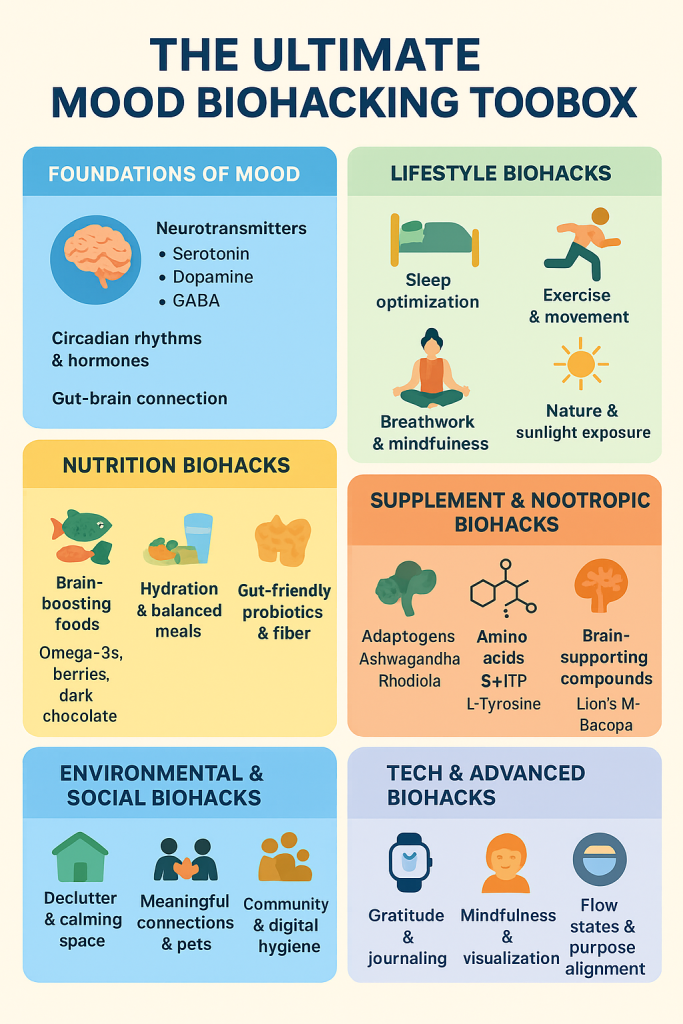
Part 1 – Foundations of Mood
What Is Mood?
Mood is more than just how you “feel” in the moment. It’s an extended emotional climate—a backdrop that influences your thoughts, behavior, and perception of reality. While emotions are often intense and short-lived (like anger or joy), mood is subtler, more enduring, and shaped by a blend of biological, psychological, and environmental factors.
Psychologists define mood as a diffuse, low-intensity emotional state that doesn’t always have a clear trigger. You may wake up feeling “off” without knowing why, or you might feel unusually optimistic despite external stress. The mystery behind mood lies in the brain–body connection, where neurochemicals, hormones, sleep cycles, nutrition, and even gut microbes play a role.
From an evolutionary standpoint, mood served as an adaptive signal. Low mood helped conserve energy and avoid risky behavior during hard times, while elevated mood promoted exploration, social bonding, and creativity when resources were abundant. Today, however, this ancient system is often hijacked by chronic stress, processed foods, and sleep disruption—leading to mood imbalances.
The Role of Neurotransmitters
At the core of mood regulation are neurotransmitters—chemical messengers that carry signals between brain cells. Each plays a distinct role, and understanding them helps explain why certain biohacks work.
- Serotonin – Often nicknamed the “happiness molecule,” serotonin regulates mood stability, sleep, and appetite. Low levels are linked with depression and irritability. Sunlight exposure, exercise, and tryptophan-rich foods (like turkey, eggs, and nuts) help boost serotonin.
- Dopamine – The “motivation and reward” neurotransmitter. Dopamine drives focus, pleasure, and goal-directed behavior. Too little dopamine can lead to apathy and fatigue, while too much creates impulsivity or addictive tendencies. Biohacks like cold exposure, novelty, and certain nootropics stimulate dopamine release.
- GABA (Gamma-Aminobutyric Acid) – The brain’s primary calming chemical. GABA helps counter stress, promote relaxation, and improve sleep. Magnesium, meditation, and L-theanine (found in green tea) enhance GABA activity.
- Norepinephrine – This neurotransmitter regulates alertness, arousal, and stress response. Healthy levels make you energized and focused, but excess norepinephrine (from chronic stress) causes anxiety and restlessness.
- Endorphins – Natural painkillers and mood elevators, released through exercise, laughter, and even spicy food. They produce the “runner’s high.”
Mood isn’t controlled by a single neurotransmitter but by their dynamic balance. That’s why lifestyle choices like exercise, diet, and sleep—which influence multiple pathways—are so powerful in mood biohacking.
The Gut–Brain Axis and Mood
You’ve probably heard of the phrase “gut feeling.” Science now shows that the gut doesn’t just digest food—it plays a critical role in emotional regulation.
- Microbiome influence: Trillions of gut microbes produce neurotransmitters like serotonin, dopamine, and GABA. In fact, about 90% of serotonin is produced in the gut, not the brain.
- Leaky gut and inflammation: Poor diet, stress, and antibiotics can damage gut lining, leading to systemic inflammation that negatively affects the brain and mood.
- Vagus nerve connection: The vagus nerve acts as a two-way communication channel between gut and brain. Practices like deep breathing, probiotics, and yoga strengthen this pathway.
Research shows people with diverse, healthy gut microbiomes are less likely to suffer from anxiety and depression. This is why nutrition (covered later in Part 3) is one of the most powerful levers for mood hacking.
Circadian Rhythms and Emotional Balance
Mood is also tied to biological rhythms—particularly the circadian rhythm, our 24-hour internal clock.
- Morning light triggers cortisol awakening response, giving you energy and alertness.
- Melatonin release at night promotes sleep and emotional reset.
- Disruption (through late-night screen time, shift work, or jet lag) destabilizes mood and increases risk of depression.
Studies show that even minor misalignments (like staying up late on weekends—“social jetlag”) can impair emotional regulation. That’s why light exposure, sleep timing, and consistent routines are essential mood biohacks.
Stress, Hormones, and Mood
Stress hormones like cortisol and adrenaline are essential in short bursts but harmful when chronically elevated. Constant stress leads to:
- Anxiety and irritability
- Insomnia
- Reduced serotonin and dopamine production
- Impaired memory and decision-making
On the flip side, hormones like oxytocin (bonding hormone) and endorphins (natural painkillers) improve emotional well-being. Activities like hugging, socializing, meditation, or even petting a dog can increase these mood-enhancing hormones.
Why Understanding Foundations Matters
Before jumping into hacks like supplements or neurofeedback, it’s essential to understand these foundations. You can’t build a strong mood without addressing the basics:
- Neurotransmitter balance
- Gut–brain health
- Circadian alignment
- Hormonal regulation
Once these pillars are solid, advanced biohacks become far more effective.
Part 2 – Lifestyle Mood Biohacks
Why Lifestyle Is the First Line of Defense for Mood
Before supplements, apps, or fancy devices, lifestyle is the foundation of mood biohacking. Your daily habits—when you sleep, how you move, what you eat, how you breathe, and even how much sunlight you get—signal your body how to regulate brain chemistry.
Think of it like building a house: lifestyle is the concrete foundation, while nootropics and technology are the paint and furniture. Without a strong base, advanced hacks won’t stick.
Let’s break down the most impactful lifestyle biohacks for mood.
1. Sleep Optimization: The Ultimate Mood Reset
Why Sleep Matters for Mood
Sleep is the body’s natural emotional reset button. Research shows sleep deprivation not only increases irritability but also reduces resilience to stress and amplifies negative emotions. Even a single bad night can impair the prefrontal cortex (the brain’s rational control center) and over-activate the amygdala (the fear/emotion center).
Chronic poor sleep is strongly linked to depression, anxiety, and mood disorders. Conversely, high-quality sleep boosts serotonin, dopamine, and GABA—all key players in balanced mood.
Sleep Biohacks
- Light management: Expose yourself to bright natural light within 30–60 minutes of waking. In the evening, limit blue light by dimming lights, wearing amber glasses, or using apps like f.lux.
- Temperature control: Keep your bedroom cool (around 18–20°C / 65–68°F). Cooler temperatures signal melatonin release.
- Sleep schedule consistency: Going to bed and waking at the same time—even on weekends—anchors circadian rhythm.
- Pre-sleep routine: Wind down with reading, stretching, or journaling instead of scrolling. This cues the nervous system to shift from alertness to rest.
- Naps strategically: Power naps (10–20 minutes) improve mood and alertness. Avoid long naps late in the day, which disrupt nighttime sleep.
2. Exercise and Movement: Natural Antidepressants
How Exercise Lifts Mood
Exercise is one of the most powerful natural antidepressants. It increases endorphins (natural feel-good chemicals), BDNF (Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor, which supports brain growth), and balances stress hormones. Studies show exercise can be as effective as antidepressant medication for mild-to-moderate depression.
Mood-Boosting Movement Biohacks
- Aerobic activity (running, cycling, swimming): Great for endorphins and serotonin release. Even 20–30 minutes can shift mood.
- Strength training: Builds confidence, improves testosterone and dopamine, and reduces anxiety.
- Yoga & tai chi: Blend movement, breath, and mindfulness—lowering cortisol and increasing GABA.
- Micro-movements: Break up long sitting periods with stretching, walking, or quick exercises. Even 5 minutes of movement can refresh mood.
💡 Hack tip: Find “joyful movement.” The best exercise is the one you actually enjoy—dance, martial arts, hiking—so it becomes sustainable.
3. Breathing & Meditation Practices
The Power of the Breath
Breathing is one of the fastest levers to influence mood because it directly regulates the autonomic nervous system. Rapid, shallow breathing increases anxiety, while slow, deep breathing activates the parasympathetic “rest and digest” system.
Breathing Biohacks
- Box breathing (4–4–4–4): Inhale for 4 seconds, hold for 4, exhale for 4, hold for 4. Used by Navy SEALs for stress control.
- Wim Hof method: Cycles of deep breathing and breath-holding combined with cold exposure. Boosts adrenaline in a controlled way, followed by calm.
- Coherent breathing (5.5 breaths per minute): Shown to balance heart rate variability (HRV), lower anxiety, and improve mood.
Meditation and Mindfulness
Mindfulness meditation strengthens the prefrontal cortex and reduces overactivity in the amygdala. Regular practice improves emotional regulation, reduces rumination, and enhances overall mood.
💡 Hack tip: If you’re new to meditation, start with just 5 minutes daily. Apps like Headspace, Calm, or Insight Timer guide beginners.
4. Nature & Light Exposure
Nature as Medicine
Spending time in nature—whether walking in a park, hiking in the forest, or even tending a garden—has profound effects on mood. Studies on forest bathing (Shinrin-yoku) in Japan show reduced cortisol, improved mood, and greater immune function.
Sunlight and Mood Chemistry
Sunlight is crucial for regulating serotonin and melatonin production. Morning sunlight exposure aligns circadian rhythm, reduces depression risk, and increases alertness.
Biohacks for Nature & Light
- Morning sunlight ritual: Get at least 10–20 minutes of sun exposure within the first hour of waking. No sunglasses or glass barriers (windows block much of the necessary spectrum).
- Midday outdoor breaks: Sun exposure around noon maximizes vitamin D production, linked with better mood and reduced seasonal depression.
- Grounding (earthing): Walking barefoot on grass, sand, or soil may reduce stress and inflammation by allowing the body to absorb negative ions. While more research is needed, many report improved calmness and connection.
5. Daily Rituals and Routines
Mood thrives on predictability. A chaotic schedule confuses your circadian rhythm and nervous system, while consistent rituals ground your day.
Ritual Biohacks
- Morning routine: Start with hydration, sunlight, and movement instead of doomscrolling.
- Evening wind-down: A fixed bedtime ritual (tea, journaling, stretching) tells your brain it’s safe to relax.
- Micro-breaks: Pause every 90 minutes to reset—deep breathing, stretching, or quick walks.
Small rituals add up to a stable emotional baseline.
6. Laughter, Play, and Joyful Activities
It might sound obvious, but many adults forget to intentionally play. Laughter releases endorphins, reduces stress hormones, and boosts oxytocin. Playfulness activates brain regions linked to creativity and emotional flexibility.
Play Biohacks
- Watch comedy or listen to funny podcasts.
- Engage in games, sports, or activities that spark fun rather than competition.
- Spend time with kids or pets—natural mood elevators.
Why Lifestyle Biohacks Work So Well
Unlike quick fixes, lifestyle biohacks work with your biology. They align circadian rhythms, optimize neurotransmitter balance, and regulate stress systems. Best of all, they’re accessible to everyone—no expensive gadgets required.
Once these are in place, supplements, nootropics, or advanced tech can build on an already stable foundation.
Part 3 – Nutrition-Based Mood Biohacks
Food as Emotional Fuel
You’ve probably felt the difference: a heavy fast-food meal that leaves you sluggish versus a fresh, balanced meal that energizes you. Food isn’t just calories—it’s information for your brain and mood. Nutrients influence neurotransmitters, hormones, inflammation levels, and even the gut microbiome.
Modern science confirms what ancient traditions hinted at: certain diets and foods can boost resilience, stabilize mood, and reduce the risk of depression and anxiety.
1. Mood-Boosting Diets
Mediterranean Diet
- Rich in olive oil, fish, nuts, fruits, vegetables, and legumes.
- Linked with lower depression rates in multiple studies.
- High in omega-3s, polyphenols, and antioxidants that protect brain health.
Plant-Forward Diets
- Diets emphasizing whole plants (vegetables, legumes, grains, seeds) improve gut microbiome diversity.
- Fiber feeds beneficial gut bacteria that produce mood-supporting compounds like short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs).
Ketogenic & Low-Carb Diets
- Some evidence shows ketogenic diets may stabilize mood by reducing brain inflammation and improving mitochondrial function.
- Useful for mood swings and neurological conditions, but may not be sustainable or suitable for everyone.
Common Threads
Across all mood-boosting diets, patterns emerge:
- Whole foods > processed foods
- Healthy fats (omega-3, olive oil, nuts) > trans fats
- Fiber-rich plants > refined carbs
2. Micronutrients That Shape Mood
Omega-3 Fatty Acids
- Found in fatty fish (salmon, sardines), flaxseeds, walnuts.
- EPA and DHA support serotonin function and reduce inflammation.
- Deficiency is linked to higher depression risk.
Magnesium
- A calming mineral that supports GABA activity.
- Found in leafy greens, pumpkin seeds, almonds, dark chocolate.
- Often called “nature’s tranquilizer.”
Zinc
- Important for neurotransmitter signaling and neuroplasticity.
- Found in oysters, beef, pumpkin seeds, and legumes.
- Low zinc is correlated with depressive symptoms.
B Vitamins (especially B6, B9, B12)
- Key for methylation processes that produce serotonin and dopamine.
- Found in leafy greens, legumes, eggs, and animal products.
- Deficiency may cause fatigue, irritability, and mood imbalances.
Vitamin D
- The “sunshine vitamin,” critical for serotonin regulation.
- Low vitamin D levels are strongly associated with seasonal affective disorder (SAD).
- Found in fatty fish, fortified foods, and produced via sunlight exposure.
3. Functional Foods & Superfoods for Mood
Dark Chocolate
- Contains flavonoids, magnesium, and compounds that increase serotonin and endorphins.
- Choose high-cocoa (70%+) varieties to avoid excess sugar.
Turmeric (Curcumin)
- Potent anti-inflammatory that may reduce depressive symptoms.
- Works best paired with black pepper (piperine) for absorption.
Green Tea
- Rich in L-theanine, which promotes calm alertness and balances caffeine stimulation.
- Also contains catechins (antioxidants) that protect the brain.
Fermented Foods
- Yogurt, kefir, sauerkraut, kimchi, miso.
- Provide probiotics that support gut–brain communication.
- Linked to lower anxiety and depression in emerging studies.
Berries
- Packed with antioxidants and polyphenols that protect brain cells from oxidative stress.
- Blueberries in particular are associated with improved memory and mood.
Coffee (in moderation)
- Caffeine boosts dopamine and alertness.
- Excess, however, can increase anxiety and disrupt sleep.
- Biohack: Pair coffee with L-theanine for smoother energy.
4. Hydration & Electrolytes
Dehydration—even mild—impairs concentration and mood, increasing fatigue and irritability. Electrolytes like sodium, potassium, and magnesium are also crucial for nerve signaling.
Hydration Biohacks
- Aim for steady water intake throughout the day, not just chugging occasionally.
- Add a pinch of high-quality salt or electrolyte mix to water if you sweat heavily.
- Monitor urine color: pale yellow = hydrated, dark = dehydrated.
5. Foods to Avoid for Stable Mood
- Refined sugar & processed carbs – Spike blood sugar, then crash mood and energy.
- Trans fats – Found in fried and packaged foods, linked to inflammation and depression.
- Excess alcohol – Initially sedating, but disrupts sleep and lowers serotonin over time.
- Ultra-processed foods – Additives, preservatives, and lack of nutrients harm gut and brain.
6. Eating Patterns & Timing
Stable Blood Sugar = Stable Mood
Mood crashes often follow blood sugar crashes. Balanced meals with protein, fat, and fiber stabilize glucose and prevent irritability.
Intermittent Fasting & Mood
- Some find that intermittent fasting improves clarity and mood via ketone production.
- Others may feel anxious or irritable if fasting too long.
- Biohack: Experiment cautiously and see how your body responds.
7. The Gut–Brain Link in Action
As covered in Part 1, gut microbes play a massive role in mood. Nutrition directly feeds or starves these microbes.
Gut-Friendly Nutrition Biohacks
- Eat a variety of fiber-rich plants (“eat the rainbow”).
- Include prebiotics (onions, garlic, bananas, asparagus).
- Add probiotic foods daily.
- Limit antibiotics unless necessary.
Why Nutrition Is a Game-Changer for Mood
Food literally becomes neurotransmitters: tryptophan from turkey becomes serotonin, tyrosine from almonds becomes dopamine, magnesium calms GABA pathways. In other words, every bite is brain chemistry in action.
Unlike quick mood fixes, nutrition builds long-term resilience by nourishing the body and stabilizing the foundations of emotional health.
Part 4 – Supplement & Nootropic Mood Biohacks
Why Supplements Can Help
Lifestyle and diet are the foundation, but sometimes the body needs an extra boost. Supplements can fill nutritional gaps, support neurotransmitter production, and help the nervous system adapt to stress.
Unlike pharmaceutical antidepressants, most natural supplements work by supporting existing pathways rather than overriding them. They’re not a replacement for medical treatment but can be powerful adjuncts.
1. Adaptogens: Nature’s Stress Buffers
Adaptogens are herbs and roots that help the body adapt to stress and maintain balance. They don’t sedate or overstimulate but rather normalize the stress response.
Popular Adaptogens for Mood
- Ashwagandha – Reduces cortisol, improves sleep, and has been shown in studies to lower anxiety and depression.
- Rhodiola Rosea – Increases resilience to stress, boosts energy, and enhances serotonin and dopamine activity. Great for mental fatigue.
- Holy Basil (Tulsi) – Traditionally used in Ayurveda for calming the nervous system and lifting mood.
- Eleuthero (Siberian Ginseng) – Supports energy and stamina while balancing stress hormones.
💡 Hack tip: Adaptogens often work best with consistent use over weeks, not as a one-time dose.
2. Amino Acids: Building Blocks of Neurotransmitters
Amino acids are precursors to neurotransmitters—the raw materials your brain needs to make serotonin, dopamine, and GABA.
- L-Tryptophan & 5-HTP
- Convert into serotonin, then melatonin.
- May help with depression, insomnia, and anxiety.
- Best taken in the evening with a small carb snack.
- L-Tyrosine
- Precursor to dopamine and norepinephrine.
- Supports motivation, focus, and resilience under stress.
- Useful before exams, workouts, or mentally demanding tasks.
- GABA (Gamma-Aminobutyric Acid)
- Direct calming neurotransmitter.
- Oral GABA’s effectiveness is debated (limited ability to cross blood–brain barrier), but many users report relaxation benefits.
- L-Theanine
- Found in green tea.
- Increases alpha brain waves, promoting calm alertness.
- Works synergistically with caffeine for smooth focus without jitters.
3. Classic Supplements for Mood
Omega-3 Fatty Acids
- Already covered in nutrition, but often taken as supplements (fish oil, krill oil, algae oil).
- Reduce inflammation and improve serotonin signaling.
Magnesium
- Supports relaxation, sleep, and stress resilience.
- Magnesium glycinate and magnesium threonate are most effective for mood and brain health.
Vitamin D
- Deficiency is strongly linked with depression.
- Supplementation often improves mood in those with low baseline levels.
Probiotics
- Certain strains (like Lactobacillus rhamnosus and Bifidobacterium longum) have been shown to reduce anxiety and depressive symptoms.
4. Nootropics: Smart Compounds for Emotional Resilience
Nootropics are substances that enhance cognitive function. Many also affect mood by balancing neurotransmitters and stress responses.
Popular Nootropics for Mood
- Bacopa Monnieri – Ayurvedic herb that reduces anxiety, improves memory, and enhances serotonin signaling.
- Lion’s Mane Mushroom – Stimulates nerve growth factor (NGF), supporting brain plasticity and emotional stability.
- Citicoline (CDP-Choline) – Enhances dopamine function and brain energy.
- Phosphatidylserine – Lowers cortisol and supports memory and focus.
- N-Acetyl Cysteine (NAC) – Antioxidant that replenishes glutathione. Shown to reduce compulsive behavior and stabilize mood.
Cutting-Edge Compounds
- Ketone Supplements (Exogenous Ketones) – Provide clean brain fuel, may improve clarity and stabilize mood.
- Peptides (like Semax and Selank) – Research chemicals with potential mood-regulating effects. Used in Russia for decades but less studied in the West.
- Psychedelic Microdosing (Psilocybin, LSD) – Emerging research shows potential for mood enhancement, neuroplasticity, and reduced depression. Still experimental and often not legally available.
5. Safety & Responsible Use
While many supplements are safe, it’s important to keep in mind:
- Individual variability – What works for one person may not for another.
- Interactions – Supplements can interact with medications. Always consult a healthcare provider if you’re on prescriptions.
- Dosage matters – More is not always better. Start low, go slow.
- Quality counts – Choose third-party tested, reputable brands.
6. Stacking Supplements for Mood
Biohackers often create “stacks”—combinations of supplements that synergize.
Example stacks:
- Calm Focus Stack: L-theanine + caffeine + magnesium.
- Stress Resilience Stack: Ashwagandha + Rhodiola + Omega-3.
- Mood Balance Stack: 5-HTP + B vitamins + magnesium.
Experimentation is key—try one change at a time and track your mood over 1–2 weeks.
Why Supplements Work Best on Top of Lifestyle
Supplements are amplifiers, not magic bullets. They work best when sleep, nutrition, and exercise are already in place. Think of them as the frosting on the cake—not the cake itself.
Part 5 – Environmental & Social Mood Biohacks
Why Environment and Social Life Matter for Mood
You can eat the cleanest diet and take the best supplements, but if your environment is chaotic or you feel isolated, your mood will struggle. Humans evolved as social, tribe-based creatures who thrived in natural environments. Today, many of us live in artificial, high-stress spaces that don’t support emotional balance.
The good news? By shaping your environment and strengthening connections, you can create a powerful buffer against stress, loneliness, and negative moods.
1. Designing Your Mood-Optimized Space
Your physical environment constantly influences your psychology—often unconsciously. Clutter, noise, and harsh lighting can increase stress, while calming, ordered spaces promote relaxation.
Environmental Biohacks
- Declutter: Studies show clutter increases cortisol and reduces focus. A tidy room = calmer mind.
- Lighting: Use warmer, dimmer lights in the evening to cue relaxation. Bright, natural light in the morning boosts alertness.
- Plants: Indoor greenery improves air quality and lowers stress. Even one potted plant can elevate mood.
- Aromatherapy: Scents like lavender, citrus, and peppermint influence neurotransmitters and promote calmness or alertness.
- Sound environment: Reduce background noise if possible. Consider white noise, nature sounds, or low-tempo music for calm focus.
💡 Hack tip: Create a “mood corner” in your home—an area with a comfortable chair, good lighting, and calming décor, reserved for relaxation or reading.
2. Music & Sound Therapy
Sound has a direct line to the emotional centers of the brain. Certain rhythms and frequencies can shift mood instantly.
Mood-Enhancing Sound Hacks
- Uplifting music: Fast tempo, major keys = energy and joy.
- Calming music: Slow tempo, soft instruments = relaxation and stress reduction.
- Binaural beats: Audio tones that entrain brainwaves. For example:
- Alpha waves (8–12 Hz): relaxation.
- Theta waves (4–8 Hz): creativity and meditation.
- Singing & chanting: Vocalizing activates the vagus nerve, calming the nervous system.
3. Social Connection as a Mood Biohack
Why Connection Is Essential
Loneliness isn’t just uncomfortable—it’s biologically harmful. Chronic isolation raises cortisol, weakens the immune system, and increases the risk of depression. On the other hand, meaningful connections release oxytocin, the bonding hormone, which counteracts stress and elevates mood.
Social Biohacks
- Prioritize quality over quantity: A few deep, supportive relationships are more powerful than dozens of shallow ones.
- Regular social rituals: Weekly dinners, group workouts, or game nights provide stability and belonging.
- Acts of kindness: Giving support boosts oxytocin and serotonin, often more than receiving it.
- Physical touch: Hugs, massage, or simply holding hands increase oxytocin and reduce blood pressure.
💡 Hack tip: If you’re introverted, don’t force extroversion. Even brief, positive interactions (like chatting with a barista) can lift mood.
4. Pets and Mood
Animals, especially dogs and cats, can significantly improve mood. Petting an animal lowers cortisol and raises oxytocin, while the responsibility of care adds structure and purpose to daily life.
- Dogs: Encourage exercise and outdoor time.
- Cats: Provide calming presence and companionship.
- Other pets: Even fish or birds can reduce stress and promote mindfulness.
5. Community & Belonging
Humans thrive in tribes. Feeling part of a community—whether cultural, spiritual, or hobby-based—creates identity and emotional safety.
Biohacks for Belonging
- Join clubs, classes, or sports teams that align with your interests.
- Engage in group volunteering for shared purpose.
- Participate in local cultural or religious gatherings if they resonate with you.
6. Digital Environment & Social Media
Social media can both connect and harm. Used mindlessly, it increases comparison, anxiety, and FOMO. Used intentionally, it maintains bonds and provides inspiration.
Digital Biohacks
- Curate your feed: Follow accounts that uplift rather than drain.
- Time boundaries: Limit social media use to set times rather than constant scrolling.
- Digital detox: Take 24–48 hours offline occasionally to reset your brain.
7. Work & Productivity Environment
Since many people spend most of their day working, the workspace heavily influences mood.
Work Biohacks
- Ergonomics: Comfortable posture reduces fatigue and irritability.
- Break design: Short breaks every 90 minutes refresh focus and prevent burnout.
- Natural elements: Adding light, plants, or even nature screensavers improves mood at work.
- Noise control: Headphones with calming music can shield from stressful environments.
Why Environment and Social Biohacks Work
The nervous system is constantly scanning the environment for safety. Safe, supportive surroundings and relationships reduce background stress, allowing mood-boosting neurotransmitters to flourish. When you align your physical and social world with your emotional goals, mood naturally stabilizes and rises.
Part 6 – Tech & Advanced Mood Biohacks
Why Technology Matters for Mood
Technology often gets blamed for anxiety and distraction—but when used strategically, it can actually enhance mental well-being. From wearable trackers that monitor stress to brain stimulation devices that fine-tune neural activity, tech offers powerful new ways to optimize mood.
This isn’t about replacing natural biohacks like sleep, nutrition, or exercise—it’s about amplifying results through targeted interventions.
1. Wearable Mood Trackers
Knowledge is power. Wearables give real-time insights into how your body responds to stress, sleep, and activity.
Key Devices & Features
- HRV (Heart Rate Variability) monitors: High HRV = resilience, low HRV = stress. Oura Ring, Whoop, and Fitbit track this.
- Sleep trackers: Devices like Oura or Apple Watch analyze sleep stages and recovery, showing how rest affects mood.
- Mood logging apps: Daylio, Moodnotes, or Bearable help you track patterns between habits and mood.
💡 Hack tip: Compare your mood logs with HRV and sleep data. You may spot hidden triggers—like how late-night snacks or arguments affect next-day emotions.
2. Light Therapy Devices
Light is one of the strongest signals for mood regulation. Too little natural light (especially in winter) can cause seasonal affective disorder (SAD).
Tech Solutions
- SAD lamps: Mimic sunlight exposure in the morning to regulate circadian rhythm and boost serotonin.
- Red light therapy: Infrared wavelengths reduce inflammation, support mitochondria, and may improve depression symptoms.
- Blue light filters: Apps like f.lux or built-in night shift modes reduce evening blue light, improving melatonin and sleep.
3. Neurofeedback
Neurofeedback trains your brain to self-regulate mood by giving you real-time feedback on brain activity.
- How it works: EEG sensors measure brainwaves; the device provides cues (like sounds or visuals) when your brain shifts into desirable states (calm, focused, positive).
- Benefits: Shown to reduce anxiety, depression, ADHD, and stress reactivity.
- Devices: Muse headband (consumer-friendly), professional neurofeedback sessions for deeper training.
4. Brain Stimulation Technologies
Electrical and magnetic stimulation can influence neural circuits tied to mood.
Options
- tDCS (Transcranial Direct Current Stimulation): Low electrical currents modulate brain excitability. Some studies show it helps depression.
- TMS (Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation): Clinically approved for treatment-resistant depression. Uses magnetic pulses to stimulate mood-regulating brain regions.
- Consumer-grade devices: Products like Fisher Wallace Stimulator and Apollo Neuro claim to reduce stress and improve sleep via gentle stimulation.
⚠️ Note: These should be used with guidance, especially medical-grade devices.
5. Cold & Heat Exposure Tech
Extreme temperatures activate the nervous system in ways that shift mood.
Cold Therapy Devices
- Cold plunges & cryotherapy chambers: Activate norepinephrine, sharpen focus, and reduce depression risk.
- Portable cold packs or shower hacks: Affordable entry point—ending showers with 30–60 seconds of cold exposure.
Heat Therapy
- Infrared saunas: Boost endorphins, enhance relaxation, and support detox.
- Traditional saunas: Linked with lower depression and improved cardiovascular health.
6. Virtual Reality (VR) & Augmented Reality (AR)
VR isn’t just for gaming—it can immerse users in calming environments or therapeutic simulations.
- VR meditation apps: Guided mindfulness in virtual forests, beaches, or space.
- Exposure therapy: Clinicians use VR to treat phobias and PTSD by safely simulating triggers.
- Mood-boosting exploration: Virtual travel can reduce stress for those unable to explore physically.
7. Smart Nutrition & Supplement Tech
Tech is making nutrition and supplementation more personalized.
- Continuous glucose monitors (CGMs): Track blood sugar spikes, helping avoid mood dips from crashes.
- Smart supplement dispensers: Timed delivery of vitamins, nootropics, or adaptogens.
- DNA testing & microbiome analysis: Identify genetic or gut-related mood factors, then customize diet accordingly.
8. Breathwork & Meditation Devices
Breath and meditation hacks become more effective with biofeedback.
- Breathing trainers: Devices like Spire or Core track breathing patterns and coach calmness.
- HRV-based meditation: Apps like HeartMath give feedback as you breathe, reinforcing calm states.
- Haptic biofeedback: Wearables that vibrate with your breathing rhythm, syncing body and mind.
9. Psychedelic Research & Future Tech
Psychedelics like psilocybin and MDMA are being studied for treatment-resistant depression and PTSD. While not mainstream biohacks yet, their integration into tech-assisted therapy is on the horizon.
- MDMA-assisted therapy: FDA-approved trials show promise for trauma healing.
- Psilocybin therapy: Can “reset” mood circuits, producing lasting improvements.
- Digital integration: Apps are being developed to guide and track psychedelic therapy sessions under professional supervision.
⚠️ Legal and medical guidance is essential here.
10. Putting It All Together
Advanced mood biohacks are accelerators. They work best when layered onto a strong foundation of sleep, nutrition, exercise, and mindset. Tech gives visibility (through data), regulation (through stimulation), and immersion (through VR or light). But balance is key—technology should serve you, not control you.
💡 Pro move: Pick one wearable, one light-based hack, and one nervous system device to test. See what shifts your mood baseline, then expand from there.
Part 7 – Psychological & Cognitive Mood Biohacks
Why the Mind Is the Ultimate Mood Hack
External factors like food, light, and supplements matter—but your thought patterns and mental habits can override or amplify them. The brain is constantly creating narratives, assigning meaning, and predicting outcomes. By consciously training these processes, you can shape your emotional baseline.
1. Cognitive Reframing
Your interpretation of events often determines mood more than the events themselves.
How to Hack It
- Identify thought distortions: Notice patterns like catastrophizing, all-or-nothing thinking, or mind-reading.
- Reframe with evidence: Ask, “What else could this mean?” or “What’s the best-case scenario?”
- Practice gratitude reframing: Even setbacks can be reframed as lessons or growth opportunities.
💡 Example: Instead of “I failed at this task,” try “I learned what doesn’t work, which puts me closer to success.”
2. Gratitude Practices
Gratitude isn’t just a feel-good cliché—it rewires the brain for positivity.
- Gratitude journaling: Write 3 things daily you’re thankful for.
- Gratitude letters: Write to someone who impacted you (send or not).
- Micro-gratitude: Notice tiny joys—sunlight, a smile, good coffee.
Studies show gratitude increases dopamine and serotonin while lowering cortisol.
3. Mindfulness & Presence
Mood often dips when the mind dwells in the past (regret) or future (worry). Mindfulness anchors you in the present.
Practices
- Mindful breathing: Focus on inhales and exhales for 5 minutes.
- Body scan: Notice sensations without judgment.
- Mindful walking or eating: Pay full attention to small daily activities.
Neuroscience shows mindfulness thickens the prefrontal cortex, improving emotional regulation.
4. Visualization & Mental Rehearsal
Athletes use visualization to enhance performance—and you can use it to elevate mood.
- Positive imagery: Visualize yourself in a joyful, successful scenario.
- Future self visualization: Imagine your best self a year from now, then embody their energy today.
- Calm rehearsal: Picture yourself handling stressful events with ease.
💡 Hack tip: Pair visualization with uplifting music to anchor the state more deeply.
5. Journaling as Mood Therapy
Writing organizes thoughts, releases pent-up emotions, and clarifies triggers.
- Free writing: 10 minutes of stream-of-consciousness to clear mental clutter.
- Problem-solving journaling: Write the problem, brainstorm solutions.
- Emotional release journaling: Write unsent letters to express suppressed feelings.
Research shows expressive writing improves immune function and reduces depressive symptoms.
6. Affirmations & Self-Talk
The way you talk to yourself shapes your identity and mood.
- Affirmations: Short, positive statements like “I am resilient” or “I choose calm.”
- Name separation: Speak to yourself in the third person (“Omar, you’ve got this”) to create psychological distance from stress.
- Replace inner critic: When you catch harsh self-talk, replace it with a supportive voice.
7. Flow State Induction
Flow is a state of deep immersion and joy in activity. Achieving flow reliably is a major mood booster.
Flow Triggers
- Clear goals and feedback.
- Balance between challenge and skill.
- Elimination of distractions.
- Full engagement in creative or skillful tasks.
💡 Hack tip: Set aside 90-minute deep work sessions where you block all distractions and dive fully into a passion project.
8. Therapy & Coaching
Sometimes the best hack is structured guidance.
- Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT): Gold standard for reframing negative thought loops.
- Acceptance & Commitment Therapy (ACT): Focuses on values-driven living.
- Life coaching: Helps with goal-setting, accountability, and perspective shifts.
Working with a professional can accelerate mood mastery beyond self-experimentation.
9. Laughter & Play
Laughter releases endorphins and lowers stress hormones. Playfulness stimulates creativity and connection.
Hacks
- Watch comedy or listen to funny podcasts.
- Schedule “play time” (sports, games, improv).
- Practice laughter yoga—yes, it works even if forced!
10. Purpose & Meaning
A sense of purpose is one of the strongest predictors of lasting happiness. Without it, mood fluctuates more with daily ups and downs.
- Ikigai exercise: Find overlap between what you love, what you’re good at, what the world needs, and what pays.
- Service orientation: Helping others provides fulfillment and boosts oxytocin.
- Values alignment: Make decisions based on core values to feel congruent and at peace.
Why Cognitive Biohacks Work
The brain constantly filters and interprets reality. By upgrading these filters—through reframing, gratitude, mindfulness, and purpose—you change not just your mood but your experience of life. Psychological hacks don’t just elevate temporary feelings; they transform your baseline outlook.
Conclusion: Building Your Personal Mood Biohacking System
Mood isn’t random—it’s a system. From brain chemistry and sleep to food, relationships, and even technology, countless factors shape how you feel on a daily basis. The empowering truth is this: while you can’t control everything in life, you can control many of the levers that influence mood.
Throughout this guide, we’ve explored:
- Foundations of mood: neurotransmitters, circadian rhythms, stress responses.
- Lifestyle biohacks: sleep, movement, breathing, nature exposure.
- Nutrition biohacks: blood sugar balance, gut health, hydration, micronutrients.
- Supplement & nootropic biohacks: adaptogens, amino acids, targeted compounds.
- Environmental & social biohacks: decluttering, light, sound, relationships, belonging.
- Tech & advanced biohacks: wearables, light therapy, neurofeedback, VR, cold and heat exposure.
- Psychological & cognitive biohacks: reframing, gratitude, mindfulness, flow, purpose.
Together, these hacks form a toolkit for emotional optimization—a way to design life for balance, resilience, and joy.
The Layering Effect: Small Hacks, Big Change
One hack alone might create a noticeable lift. But the real transformation comes when you stack habits. Sleep well, move daily, eat brain-friendly foods, connect socially, and use tech to track progress—suddenly, your baseline mood rises dramatically.
This is the compounding effect of biohacking. Just as compound interest grows wealth, stacked hacks grow emotional resilience.
Experiment, Don’t Perfect
It’s easy to feel overwhelmed by options. The key is not to try everything at once but to approach mood hacking as an experiment.
- Pick one hack from each category—say, morning sunlight (lifestyle), more omega-3s (nutrition), ashwagandha (supplement), journaling (cognitive), and a wearable for HRV tracking (tech).
- Run it for 2–4 weeks. Track your mood.
- Keep what works, discard what doesn’t, and layer in new hacks gradually.
Think of yourself as a scientist of your own mind and body.
Mood as a Foundation for Everything Else
When your mood is optimized, everything else improves: productivity, creativity, relationships, health, and decision-making. A stable, positive mood doesn’t just feel good—it helps you show up as your best self in work, love, and life.
That’s why mood hacking isn’t just self-care—it’s a form of life optimization.
A Final Word
Mood biohacking isn’t about chasing constant euphoria. No one feels amazing every second of every day. Instead, it’s about raising your baseline so that even on tough days, you have tools to stabilize and recover quickly. It’s about building emotional resilience, not perfection.
Your mood is both your compass and your fuel. By learning to influence it—through sleep, food, supplements, environment, tech, and mindset—you gain control over one of life’s most powerful forces.
So start small. Try one hack today. Notice the shift. Then build, layer, and refine.
Over time, you won’t just be “managing mood”—you’ll be mastering it. And with that mastery comes not just happiness, but the clarity, energy, and purpose to live fully.
What Japanese Brain-Scan Research Reveals About Gymnast Neuroplasticity
An illuminating study reported by The Asahi Shimbun reinforces this deep dive into neuroplastic changes in Olympic-level gymnasts—which aligns perfectly with our core topic.
Researchers led by Hidefumi Waki at Juntendo University conducted MRI scans on 10 male gymnasts with world-class credentials and compared them to a control group of non-athlete males. Strikingly, certain regions of the gymnasts’ cortex were about 10% larger—notably the precentral gyrus (motor function) and the inferior parietal lobule (involved in spatial perception and sensory integration) 朝日新聞.
Furthermore, the team discovered that athletes with higher average competition scores tended to have larger volumes in the inferior parietal lobule, suggesting that long-term training reshapes brain regions tied to spatial and sensory processing 朝日新聞. Interestingly, no regions were found to be smaller, underscoring that these adaptations appear to be built—not traded off.
Waki notes that gymnasts’ ability to make split-second body adjustments—even before initiating movement—is central to their expertise 朝日新聞. These insights dovetail with our discussion on prefrontal recalibration, motor-visual integration, and the emergence of autopilot-like performance in elite athletes.
Shaolin monks brain scan research not only highlights incredible focus and resilience but also connects deeply to modern health and wellness practices. Their disciplined lifestyle—balancing meditation, movement, and mindfulness—shows us how ancient wisdom aligns with today’s science-backed approaches to stress management, emotional regulation, and overall well-being.